When you digitally sign an application (a process known as code signing), you assure users that the code has not been tampered with or altered. Digital signing is based on Microsoft Authenticode® technology. This enables both users and the operating system to verify that the program code comes from the legitimate publisher. ExeOutput for PHP makes it easy to sign your compiled application .exe files by calling the necessary programs automatically.
If you digitally sign your software, users are generally presented with a digital certificate when they download your application:
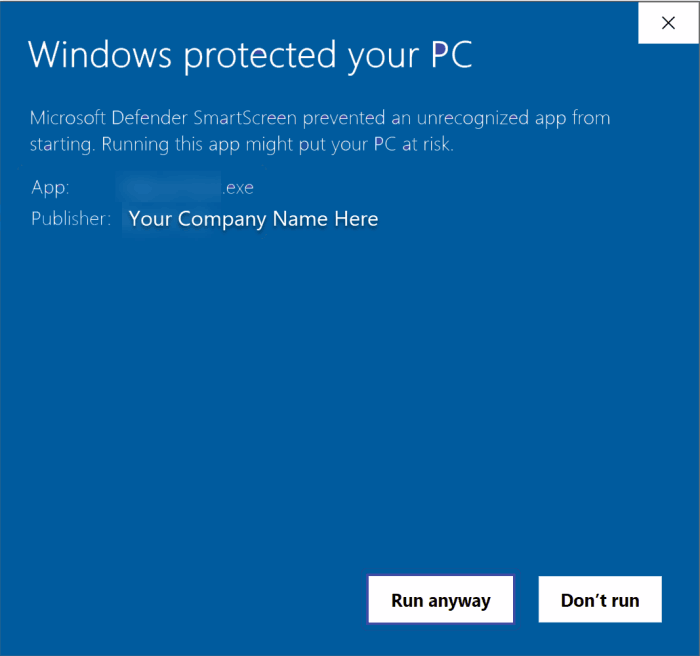
For signed applications, the publisher’s name is displayed. Your users will know that the .exe file is authentic and has not been tampered with.
For unsigned applications, Windows shows the following warning message:
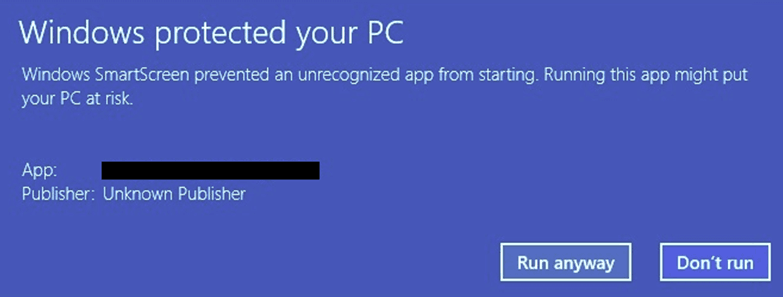
To digitally sign your application, enable the “Digitally sign my application” option in Security -> Code Signing and follow the steps below.
Info
This Microsoft article explains most of what you need to know about code signing with Authenticode: Introduction to Code Signing
Warning
Current Windows limitations prevent the signing of EXE files larger than 2 GB. If code signing is a requirement and your EXE file exceeds 2 GB, consider keeping some files external.
How to Obtain a Code Signing Certificate #
To sign your application, you need a valid code signing certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), such as Sectigo or DigiCert. CAs offer different types of certificates, but only code signing certificates are compatible with Authenticode.
You can only digitally sign your .EXE after you have received your certificate and token from a CA.
Steps for Code Signing #
ExeOutput for PHP simplifies the code signing process with its integrated GSignCode.exe utility. No third-party software installation is necessary. Follow these steps to sign your application:
- Specify the location of your code signing certificate, either by providing the path to the Personal Information Exchange (PFX) file or by selecting the certificate from the Windows Certificate Store (Local Computer, Personal section). You must provide either the path to the PFX file, the certificate’s subject name, or the certificate’s thumbprint.
- If using a PFX file, enter the associated password for added security.
- Alternatively, specify the certificate’s subject name or thumbprint for direct access from the Windows Certificate Store.
Application Information URL #
This URL is included in your digital certificate to direct users to a webpage where they can learn more about your product or company. If you do not specify a URL, ExeOutput for PHP will use the default from the Icon / Version page.
Code Signing with a Token #
Following changes implemented by the Certificate Authority/Browser (CA/B) Forum, effective June 1, 2023, the code signing process has shifted significantly. The forum now mandates that code signing certificate keys be stored on a hardware security module (HSM) or a token that meets or exceeds FIPS 140-2 Level 2 or Common Criteria EAL 4+ standards. This change is primarily aimed at combating the malicious use of stolen code signing keys to sign and distribute malware.
With this new requirement, the traditional PFX (Personal Information Exchange) format, which can be stored and accessed digitally, is becoming obsolete. Instead, it is recommended to use the subject name or thumbprint of the certificate after installing it (as a .CER file) in the personal Windows certificate store.
ExeOutput for PHP handles code signing with a required token without issue. Just ensure the token containing the private key is physically inserted into the computer.
Tip
If your CA uses the SafeNet client, you will be prompted for your password with each code signing instance. To streamline this process, you can activate the “Enable single logon” option. This setting requires the password to be entered only once per session, rather than for each signature, thereby reducing redundancy.
Digest Algorithms #
While SHA-1 is being deprecated due to security vulnerabilities, newer algorithms like SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512 are recommended for stronger security. They are supported across all modern Windows systems. It is important to note that SHA-1 is also being deprecated and should no longer be used for code signing. Please choose the algorithm that meets your CA’s specifications.
Dual Code Signing (SHA-256 and SHA-1) #
It is now mandatory to use signatures with an SHA-256 message digest instead of SHA-1. However, older Windows versions like Vista or XP do not recognize SHA-256 signatures. In this situation, it is possible to add two signatures to the .EXE file in a process called “dual code signing”.
Warning
By default, ExeOutput for PHP will use dual code signing if run on Windows 8 or later. On Windows 7, an SHA-256 signature is used by default, and on previous Windows versions, an SHA-1 signature is used. Therefore, we recommend using ExeOutput for PHP on Windows 8 or higher to benefit from all code signing features.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) Support #
In addition to RSA, ExeOutput for PHP now supports certificates that use Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). ECC certificates offer stronger security with shorter key lengths, making them more efficient. For instance, a 256-bit ECC key provides security comparable to a 3072-bit RSA key, enhancing both performance and security.
Digital Signature Timestamp #
A timestamp is added to your application’s digital signature to ensure it never expires, even after the signing certificate has expired. Ensure your system has an internet connection during the signing process for this time-stamping to work.
Two timestamp servers are used: an Authenticode-compatible server and an RFC-3161-compatible server. You can configure their URLs in the Environment Options.



