You can access the File Manager by clicking its ribbon at the top. It allows you to manage all files to be compiled into your application and behaves like Windows Explorer.

You get a global view of your application’s contents. The Folder tree displays the available subfolders, similar to using an FTP program to manage files on a server.
To view a folder’s contents, simply select it in the Folder tree, and its contents will be listed. Note that ExeOutput for PHP may take a few seconds to load the entire file list when displayed for the first time, especially if the subfolder contains a large number of files.
The index page is indicated by a small house icon (as shown in the screenshot). Excluded files are marked with a red cross.
Selecting the All Files (real paths) node in the Folder tree will list all files to be compiled with their full path. Selecting the All Files (virtual paths) node will list all files with their virtual path (i.e., the path that follows the server or domain name in a URL).
Warning
ExeOutput for PHP stores file relative paths in projects. Once a project is started, you may need to move source files to another directory. In some cases, ExeOutput for PHP may prompt you to select the new source folder, and the program will attempt to correct all file path references. It will refuse to compile a project if any files are missing.
About Virtual Paths #
Virtual paths are paths that follow the server or domain name in a URL. We use virtual paths in applications because they function like servers: to access a compiled file, you need to use its URL. For instance, if you have the URL: ghe://heserver/images/picture1.gif
https://heserver/(for CEF) orhttps://heserver.example/(for WebView2) refer to the custom internal protocol and namespaces used by ExeOutput for PHP to display files in the custom browser. Theghe://protocol is also an alias.imagesis the virtual path.picture1.gifis the filename.
Note that ExeOutput for PHP automatically manages virtual paths (see below); all features related to virtual paths are designed only for advanced users.
Adding Virtual Folders #
To add empty virtual folders to your application, click Add and then Add Virtual Folder. You will be prompted to enter its name, and it will then be created as a child of the selected folder (if no folder is available or selected, it will be created as a child of the application root). You can then move files to this folder using drag-and-drop operations.
Warning
Important: If you do not place any files inside an empty virtual folder, it will be automatically removed the next time your project is loaded.
Managing Files #
All source files are generally added automatically when ExeOutput for PHP creates your project. However, you can manually add new files, folders, or source wildcards to your list at any time. Alternatively, let ExeOutput for PHP perform this task automatically using the powerful Source File List Update option.
You can manage your files using the button bar below or the right-click context menu on the file list:
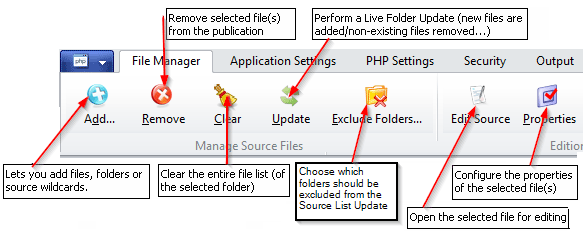
Adding Files #
To add files to the list, click the Add button and select an option. You can add single or multiple files, entire folders, virtual folders, and custom wildcards. Just select the appropriate action after clicking the Add button:
- Add Files
- Add Folder
- Add Source Wildcard
- Add Virtual Folder
For example, selecting “Add Wildcard” will open this window:
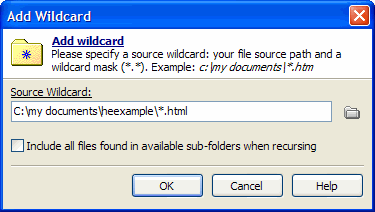
You can enter a path and specify which files should be added using a mask. In the situation shown in the screenshot, only .html files from C:\my documents\heexample will be added. Alternatively, you can add entire folders (including their subfolders or not) using the “Add Folder” command.
When added files are not in the source folder or one of its children, you need to specify the application path (also known as the virtual path) that should be used to access these files once they are compiled into the application. ExeOutput for PHP lets you determine these virtual directories using the following window (which is automatically shown when adding files):
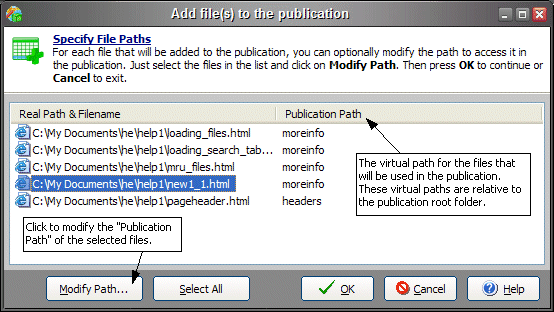
The real paths appear on the left; on the right, you can determine the related virtual path (also known as the application path). By default, ExeOutput for PHP attempts to find the best virtual paths, but you can change this yourself. Just select one or more files, then click Modify Path. You will be prompted to enter the new virtual path and confirm your changes.
Once you click OK, ExeOutput for PHP adds them to the application’s file list, and the result is:
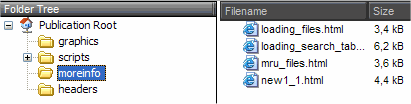
You can see that the virtual paths moreinfo and headers appear as children of the application root, even though the added files do not belong to the source folder.
Success
This option is powerful because you can add files from any folder and determine virtual paths yourself. The main advantage is that you do not need to copy the source files to the source folder before compilation.
Drag-and-Drop Operations #
ExeOutput for PHP supports drag-and-drop operations:
- From Windows Explorer and other shell windows: Select all the files in Explorer, drag them onto the manager’s file list, and they are automatically added. You may be prompted to enter the virtual path for the dropped files, as explained above. You can launch Windows Explorer by clicking the Explorer button.
- Within the File Manager: You can move files from one virtual folder to another, thereby changing their virtual paths as desired. Highlight the file(s) you want to move in the list, then drag and drop them onto the destination folder in the Folder Tree. Note that real paths are not modified (source files are not physically moved).
Removing Files #
To remove one or more files from the list, select them and click the Remove button. You can select multiple files by pressing Ctrl+Click or Shift+Click. You may also use the Select All menu command from the context menu.
Finally, the Clear button lets you remove the entire folder currently selected in the Folder Tree. This includes all files and subfolders within that selected folder. This operation cannot be undone, so proceed with caution. It is also useful for removing empty folders.
Notes:
- You cannot remove the index page from the application.
- You cannot clear the application root; use the Remove operation instead.
- Removing files does not delete them from your hard disk; it only removes them from the application.
Sorting Files #
ExeOutput for PHP displays information about each file, including filename (or file path/virtual path), file type, and size. If you need to sort your files according to a specific criterion (for example, file types), click the associated column header. You can also resize the columns.
Source File List Update Operation #
Generally, source files need to be updated. You can add new files to the source folder, update existing ones, or remove unused ones. In other words, the contents of the source folder may vary, and consequently, the file list maintained by ExeOutput for PHP may become outdated.
You can, therefore, use the File List Update action. This action forces ExeOutput for PHP to scan the source folder (and its subfolders) and detect all changes. It then compares the results and determines the appropriate actions:
- If new files are found (not in the file lists), they are added. You can optionally be prompted to specify the new virtual paths (see the Environment Options).
- If source files are newer, ExeOutput for PHP updates its file lists.
- If source files are not found (e.g., they were deleted), they are removed from the file lists. You can also be prompted to confirm the operation (see the Environment Options).
Consequently, you do not need to manage the file lists manually.
There are several ways to trigger a File List update:
- Click the Update button in the File Manager.
- Configure automatic File List updates using the Environment Options.
- You can manually indicate which subfolders should be excluded from the File List update by clicking Exclude Folders and adding full paths to the folders you want to exclude to the dedicated list. You can also exclude some files from being added to the file list based on their extension. Go to the Environment Options.
Notes:
* File List Update only accounts for files in the source folder (or subfolders). If you have files from other folders, the operation will ignore them.
* Hidden files are automatically excluded: Files with the “hidden” attribute are not included during a file list update.
Editing Files #
Select a file in the list and click the Edit button.
- If the selected file is a PHP or HTML-compatible page, the internal PHP/HTML editor will be displayed.
- Otherwise, the program registered with the file will be opened to edit it (this is equivalent to double-clicking the file in Windows Explorer).
More information about the internal PHP/HTML editor
Setting Folder, File, and PHP/HTML Page Properties #
You can configure options regarding compression and security for source files (and even entire folders). Select a folder or file in the list and click the Properties button (or double-click it). The file properties editor will then be displayed.
More information about the file properties.
Using the Context Menu #
All of the previous commands are also available from the context menu. Right-click the file list to display it. It contains additional commands not directly available, such as “Select All” or “File Information”. The last command provides global information about the application files in the selected folder (total size, number of files, etc.). Finally, the “Shell Properties” command will display the “Properties” dialog available in Windows Explorer (allowing you to access the properties of the selected file).



