File compression and security properties can be edited via the File Manager. To edit properties, select one or more files, then click Properties (or press Ctrl+P). The following window will appear:
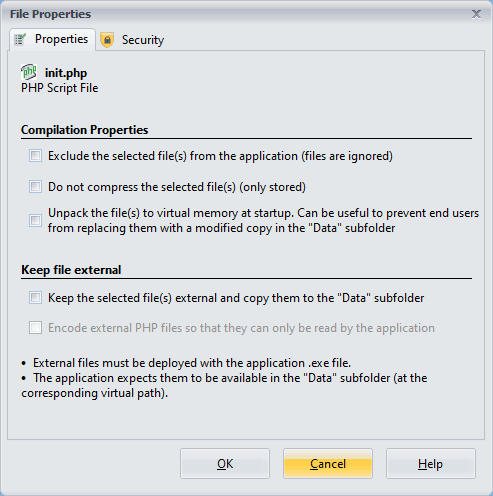
If the selected file is a PHP script, you will see two tabs: Properties and Security. For other file types, only the Properties tab is available.
The name and type of the selected file will be displayed, or “Multiple files” if several are selected. Hovering over the filename will show the full path to the file in a tooltip.
Folder Properties #
You can also set properties for an entire folder: select a folder in the Folder Tree and click Properties. The “Folder” window will appear:
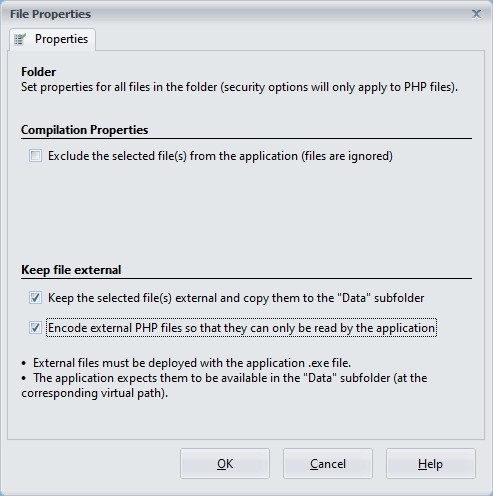
For folders, you can apply property values to all files and subfolders within. For example, excluding a folder will automatically exclude all contained files and subfolders.
Warning
Folder properties override individual file properties. If a folder is set to be kept external, individual file settings within that folder cannot be altered. In such cases, ExeOutput will disable the corresponding checkbox.
File Properties #
Compilation Properties #
- Exclude the selected file(s): If enabled, ExeOutput for PHP will exclude the file from compilation, making it completely unavailable. Excluded files are marked with a red cross in the File Manager.
- Do not compress the selected file: If this option is enabled, ExeOutput for PHP will compile the file but not compress it. The file is stored uncompressed in the application’s data folder. This option is beneficial for including files that are already compressed.
- Unpack the file(s) to virtual memory at startup: This option unpacks the file to virtual storage (the virtual
Datasubfolder within the folder where the EXE is located) when the application starts. The file is unpacked to memory, not to the hard disk, and can be accessed by PHP as if it were a regular file on the disk. This is akin to the internalexo_unpackvirtualfilePHP function. This setting helps prevent users from substituting PHP files with altered versions in theDatasubfolder.
Keep File External and Copy to the “Data” Subfolder #
To avoid the unpacking process, large files or folders with many files can be kept outside the application’s .EXE file. These files are then loaded directly from the “Data” subfolder, which significantly reduces loading times.
If this option is enabled, ExeOutput for PHP will automatically copy the external files to the designated location in the Data subfolder.
Important
Existing external files in the destination folder will be overwritten by ExeOutput for PHP if the source file is more recent than their copies in the destination folder.
External files must be deployed alongside the application’s .exe file. Installers generated by ExeOutput for PHP can include external files in the Data subfolder.
Encoding External PHP Files for Enhanced Security #
ExeOutput for PHP allows you to encrypt external PHP files, ensuring that their contents can only be accessed by the application and remain hidden from users.
The downside is that external files will be encrypted during each application compilation, extending the compilation time when encryption is used.
Note
This encryption feature is specific to PHP files; non-PHP files are not affected.
See also: File Properties Editor
Security #
This tab offers two security features specific to PHP.
Protection Marks #
You can mark selected PHP files for additional protections, such as internal encoding. These protections must be enabled in the PHP settings ribbon to take effect.
Encode PHP file with internal protection: This option encrypts the PHP file’s content at compilation, ensuring it remains encrypted in memory even at runtime. This is beneficial for protecting your PHP source code from being exposed during a memory dump.
The “Do not cache PHP source file in memory” option is incompatible with the Unpack the file(s) to virtual memory at startup setting.



